Desktop Excel has a row limit of 1,048,576 rows and a column limit of 16,384 columns. The Excel row limit exists because desktop Excel runs locally on a user's computer and is limited to the memory (RAM) and compute (CPU) resources on the computer. Spreadsheets perform both data storage and analysis in one application, which requires greater memory usage. As data sets have grown, it has become more common to encounter Excel's row limit. In fact, other spreadsheets, like Google Sheets and Apple Numbers, also have row limits.
In the post below, we provide 5 solutions for working with big datasets that exceed the Excel row limit. If you are looking for a quick solution, try Row Zero, a next-gen spreadsheet built for big data that can handle giant billion row datasets (1,000x Excel's row limit) and complex models. Continue reading or use the table of contents to skip to specific sections.
- 5 solutions to the Excel row limit
- What is the row limit in Excel?
- What is the column limit in Excel?
- The effects of hitting the Excel row limit
- Why does Excel have a maximum number of rows?
- Conclusion
Desktop Excel is exceptionally fast when data sets are small to medium sized. However, Excel starts to slow down well before the row limit is hit. We wrote about the symptoms of slow Excel spreadsheets in a previous post. For datasets larger than the maximum number of rows, the size is an obstacle and as the world accumulates more data, users will more frequently hit Excel's performance limits.
5 Solutions to the Excel row limit
The following list details the best options for overcoming the row limit in Excel. These options will help you use advanced features in Excel, utilize other tools to store or shrink your data before importing to Excel, or use a more powerful spreadsheet that acts just like Excel but is built for large data sets.
1. Use a More Powerful Spreadsheet
The simplest solution to the Excel row limit is to use a more powerful spreadsheet. Row Zero is a big data spreadsheet that works like Excel but can handle billion row datasets (1000x Excel's row limit). Row Zero runs in the cloud and is not hamstrung by the hardware on a user's computer. You can ingest data from a csv upload, S3 import, database query, API connection, or a connection to any other cloud data source. Row Zero's spreadsheet is free to try and easily handles millions of rows on the free plan, making it the best Excel alternative for big data users.
2. Data Model/PowerQuery
Microsoft built a few additional features into Excel to let users work with large datasets. Those features are Data Model, Power Query, and PowerPivot. These features enable a user to open a 1M+ row dataset and view the first million rows, sort, filter, and pivot.
Data Model, Power Query, and PowerPivot are hard to find but they exist for the big dataset use case. The downside to these features is they don't facilitate the interactivity a spreadsheet provides. Interactions are limited to column level computations and it's not easy to build models as you normally would with data sets below the row limit in Excel.
Follow instructions below to use them.
- Click the 'Data' menu across the top, then select 'Get Data.'
- Then select the data type you would like to import and click 'import.'
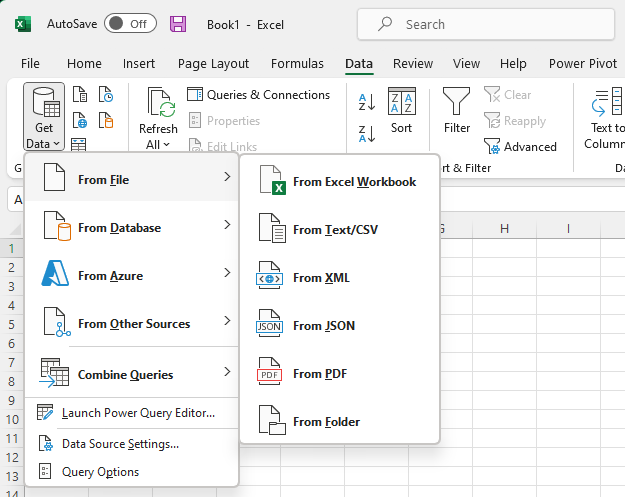
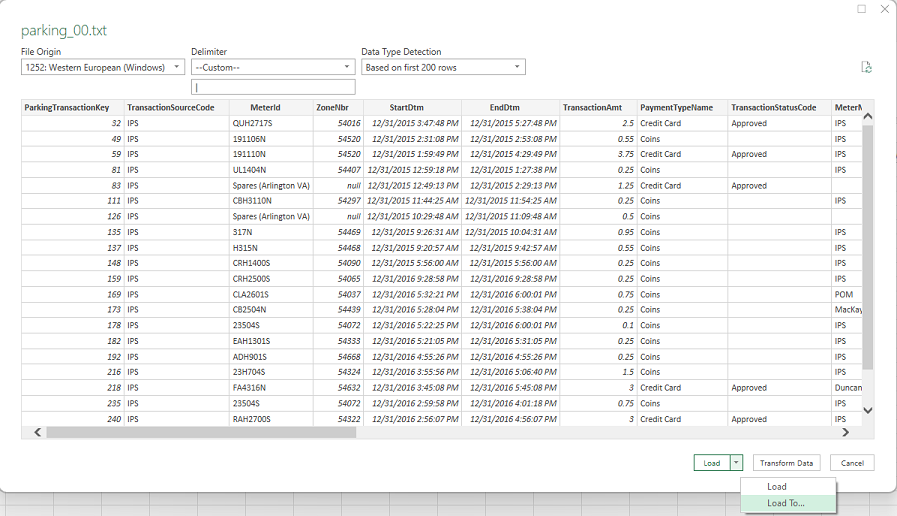
- Once the preview launches, select 'Load to' from the bottom drop down.
- You will see several options
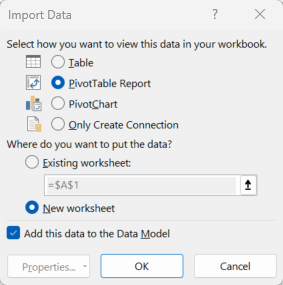
- Pivot table - Allows interactions with the data in a pivot table format but the underlying data is not visible
- Pivot chart - Allows pivot interactions with the data, which generates a chart. The underlying data is not visible.
- Table - Tries to load data to a worksheet but will only display the first 1,048,576 rows (the maximum rows Excel supports).
- Only Create Connection - Creates a connection to the data set. Data can be viewed by clicking on 'Manage data Model' or double clicking the data connection. Make sure in each case you select 'Add this data to the Data Model,' otherwise the workbook won't support more rows than the Excel max row limit.
3. Use a Jupyter Notebook
- Jupyter Notebook - Jupyter is a tool best suited for software engineers, data scientists, and analysts that know how to code. The application enables manipulation of large data sets with commands written in code cells commonly in python, R, or SQL and can handle millions of rows, though it runs locally and is dependent on the hardware in a user's computer. Notebook users still may notice slow performance when doing complicated analysis on giant data sets but the program likely won't freeze or crash, like Excel.
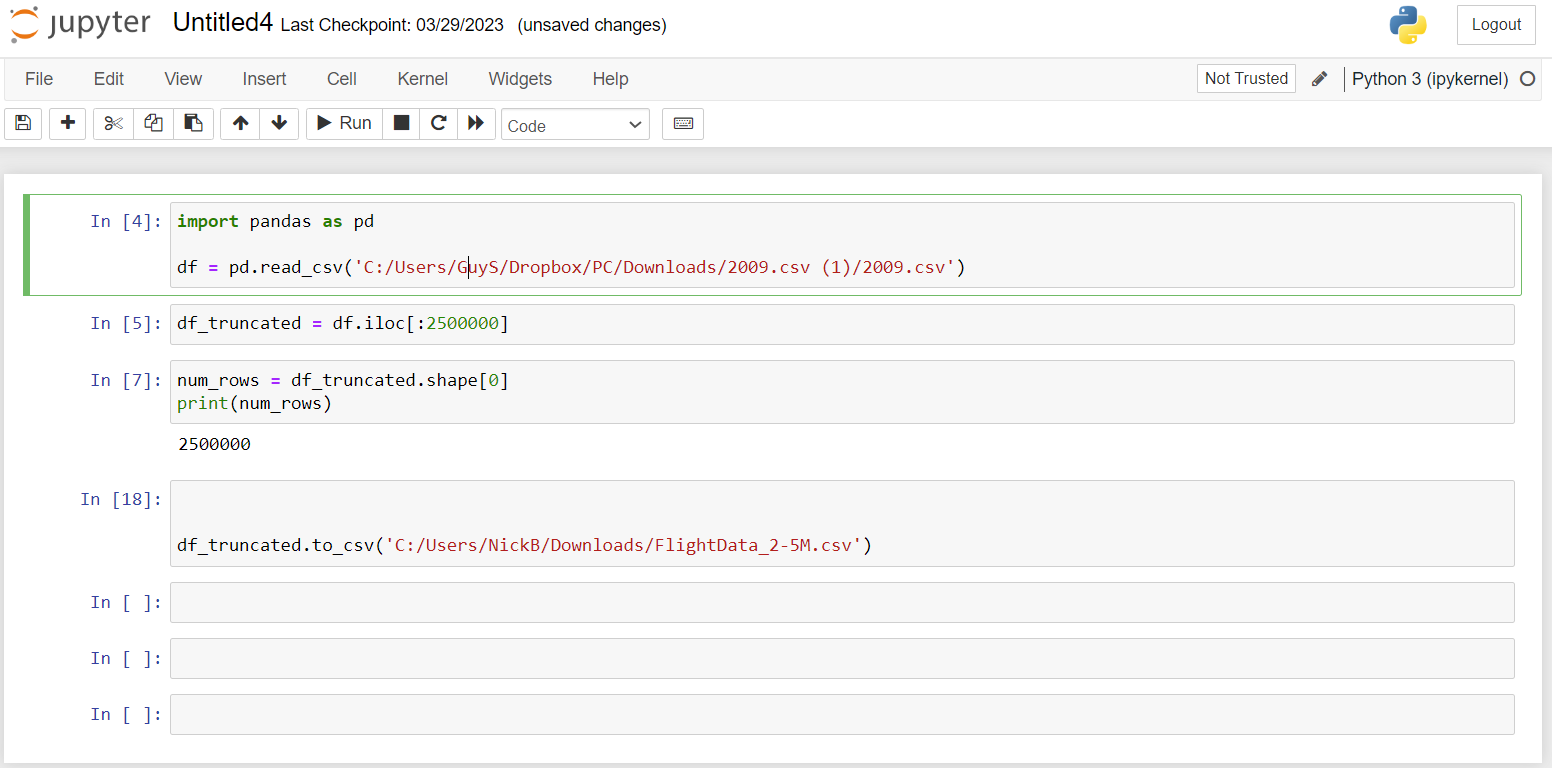
4. Use a SQLite Database
- SQLite - SQLite is an easy to install lightweight database that can be installed and run on a user's computer. The database can store millions of rows of data, which can be accessed by writing SQL queries to transform and analyze data. Once transformed to a smaller subset that is below Excel's data limits, the data can be opened in an Excel spreadsheet.
5. Open in a large file editor and trim or split your file
You can open files too big for Excel in another program and either delete all the rows over 1,048,576 so it can be opened in MS Excel or you can split large files into multiple smaller files that are under the Excel file size limit. Here are some programs you can use to open and edit large files:
Row Zero: Row Zero lets you open and edit billion row data files too big for Excel. Once you open your file in Row Zero, you can do whatever spreadsheet work you want and then if you need to get it back to Excel, you can trim or split your spreadsheet below 1 million rows to get it under the Excel max row limit. Then export to CSV so you can re-open in Excel.
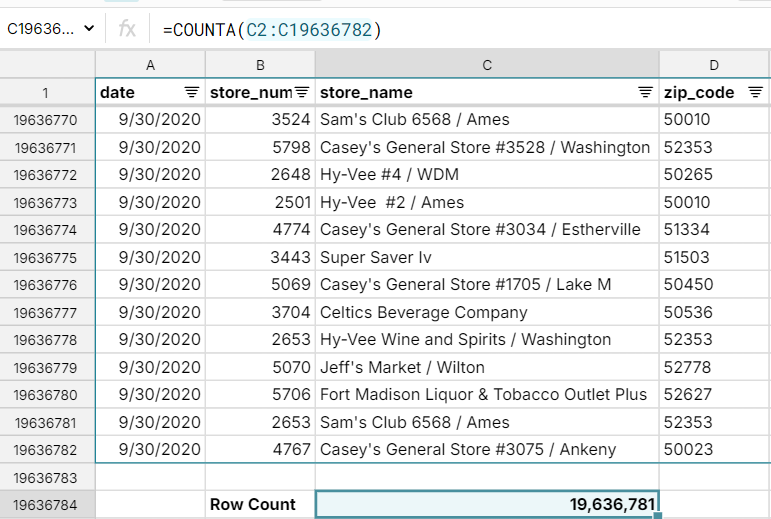
Notepad++: Notepad++ is a simple, yet powerful text editor that lets you open large files. Once you open your file you can split it into multiple files or delete rows below above the Excel maximum row of 1,048,576.
What is the row limit in Excel?
Excel limits the number of rows it displays to 1,048,576 rows. Note this is the Excel sheet limit. Workbooks can theoretically have multiple worksheets that hit the maximum sheet in Excel. However, in practice Excel will likely slow down, freeze, or crash at these data sizes. Here's how the Excel row limit compares to other spreadsheets:
What is the column limit in Excel?
Excel limits the number of columns it displays to 16,384 columns. Typically Excel users hit the max row limit in Excel before they hit the Excel column limit because big data sets tend to be longer than they are wide. That being said, hitting the column limit does happen. Going out 16,384 columns, the Excel max column is XFD.
What are the effects of hitting the Excel row limit?
When trying to import or open a data set in an Excel worksheet that exceeds the maximum number of rows, Excel will alert the user that the data set is too large for the Excel grid. 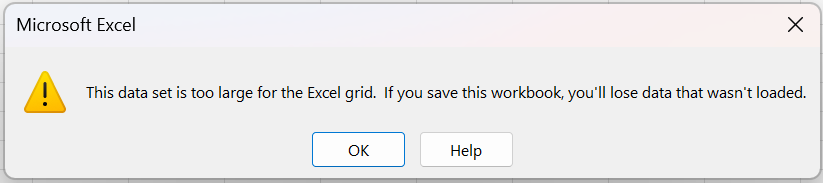
If 'ok' is selected, Excel will proceed with importing the data set but will truncate any rows beyond Excel's maximum row number of 1,048,576. 
Once the data is in, Excel may perform well if the computer being used has sufficient memory (RAM). If the computer has insufficient memory, a number of performance deficiencies will manifest. A more detailed overview of Excel's performance issues can be found in the blog Why is excel slow or slow to open?. Among other things, working with large data sets, even if they are under Excel's max rows, can cause Excel to crash, run slowly, or cause an inability to save the file. If you're struggling with Excel's capacity limits, try one of the solutions above.
Why does Excel have a maximum number of rows?
Excel stores data in a grid format, with each cell having its own unique address based on its row and column position. Each cell can contain a certain amount of data, such as text, numbers, or formulas, and this data is stored in memory. As the number of cells in a worksheet increases, so does the amount of memory required to store and manage that data.
In addition, Excel needs capacity to perform calculations and manipulations on that data, such as sorting, filtering, and creating charts. These operations require processing power, and as the amount of data increases, so does the amount of processing power required.
Excel runs locally on a user's computer and is therefore constrained by the amount of memory (RAM) and processing power (CPU) on the machine. The performance of Excel and its ability to handle large data sets and perform big computations is therefore limited by the hardware on the computer. The average computer has 8GB of RAM and with large data sets and lots of functions, that memory will get consumed quickly. Computers with more RAM (16GB or 32GB) will perform better and faster processors will enable the spreadsheet to perform more calculations per second. At the largest row count of 1,048,576, Excel ceases to be responsive due to the amount of memory required to support all the data and features to manipulate it. In addition to row count, functions that scan entire columns of data or execute row level computations over a large number of rows will slow down or crash an Excel spreadsheet. Additionally, the row limit is 2^20 which is the max number of rows that can be represented in a 32 bit system. Excel 64 bit has the same row limit but better performance.
Conclusion
There are a number of different options for working around Excel's row limit. Most of them require learning some new skills, downloading programs, or file manipulation. If you are comfortable writing code or SQL you can use a jupyter notebook or SQLite database to work around the Excel max row limit. If you would prefer to stick with existing tools, some of Excel's work-arounds may be sufficient. In our opinion, the easiest option is to simply use a better spreadsheet than Excel for big data needs. Row Zero is a powerful spreadsheet built for big data which you can try for free.
Another solution to Excel's capacity limits would be the use of a BI tool, like Microsoft's PowerBI or Tableau business intelligence tools. Both tools are feature rich and powerful visualization and BI tools. These tools are very different from the spreadsheets most people are familiar with and for that reason, were not reviewed in this post.